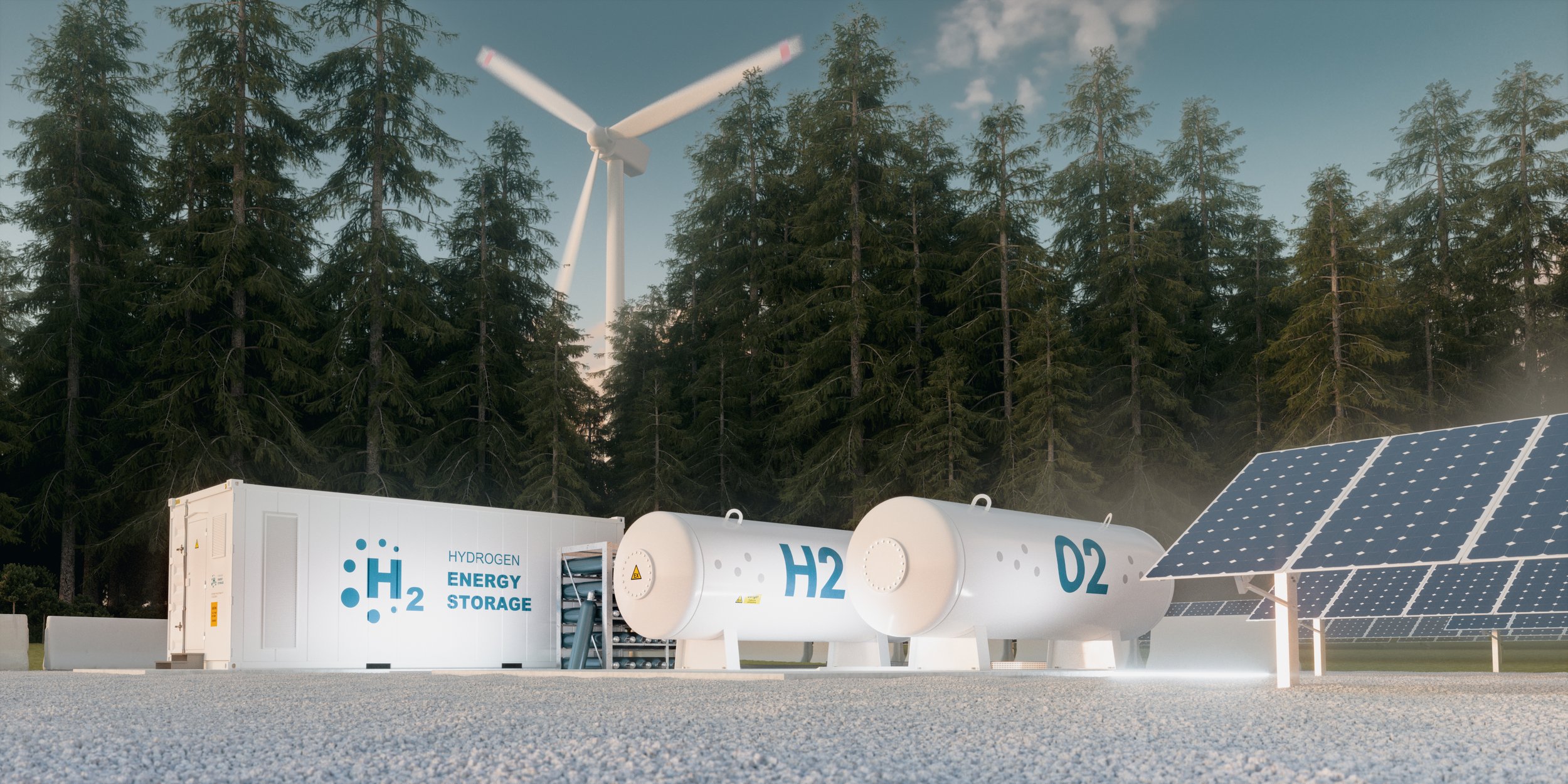
Adoption of hydrogen energy is key to ending fossil fuel dependance
Hydrogen is a versatile energy carrier with a very good energy density. It is the key to bringing about a greener economy and phasing out the fossil fuels that are destroying the planet.
Not all hydrogen is green, as currently 99.6% of the hydrogen produced worldwide comes from fossil fuels such as natural gas reformation and coal gasification.
Renewable energy has progressed so much technologically that green hydrogen via electrolysis is now a viable alternative.
What problem does it solve?
Since the era of industrialization, hydrocarbons have been used to produce, store, and transport energy.
Green production is possible by renewable energy technologies such as wind turbines and solar panels whose levelized energy cost has been declining rapidly and now is less the cost of fossil fuel plants.
Storage and Transport
Hydrogen offers a viable green alternative to oil and gas as it is energy-rich, can be produced from water via renewable energy, and is stored and transported with little extra cost.
-
Green Energy Distribution
Hydrogen can be transferred from renewable energy rich countries to countries with poor renewable energy conditions that currently depend on fossil fuels.
-
Renewable Generation Buffer
Hydrogen can help store green energy when supply is higher than demand and prices are cheap, or when demand is high but wind or sunlight low.
-
Mobility
Hydrogen’s high energy density makes it a powerful fuel that could power transportation from not only cars and trucks to the entire shipping industry.
Types of Hydrogen
-
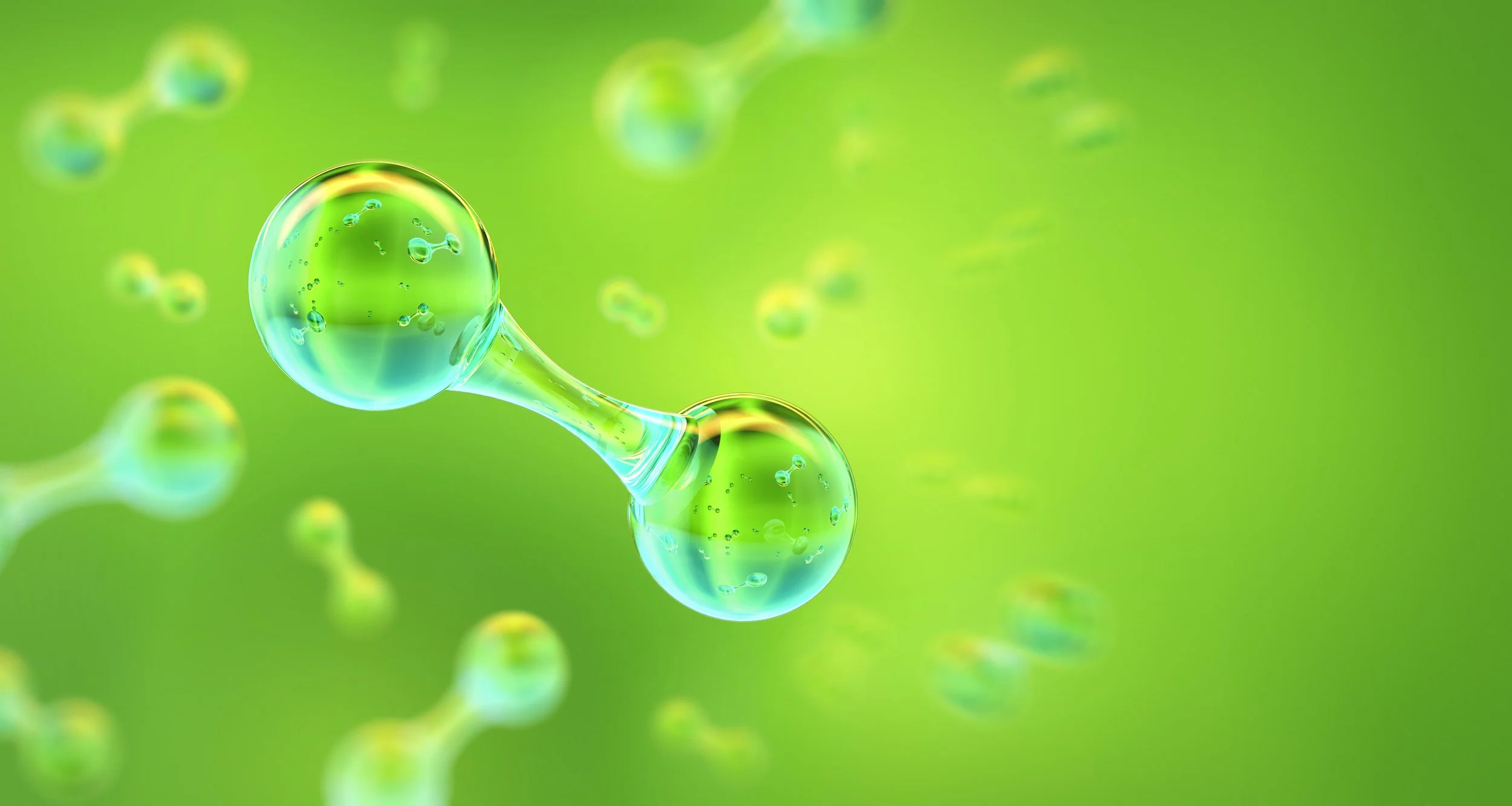

Green Hydrogen
Obtained by splitting water into oxygen and hydrogen via electrolysis, this process uses electricity gathered from renewable sources.
-

Grey Hydrogen
Grey hydrogen is obtained from natural gas by a process called steam reforming, which releases carbon that is stored in the natural gas.
-
Blue Hydrogen
This comprises the same process as grey hydrogen, but the carbon emissions are then captured and stored.

Hydrogen can be stored as:
Compressed hydrogen
Can be compressed to between 350 and 700 bar.
Liquid hydrogen
Can be stored as a liquid at -253°C.
Light chemical
Such as ammonia, methanol, ethanol. For example, hydrogen can be mixed with nitrogen, through a Haber-Bosch process to produce ammonia.
Ammonia provides the best storage and transportation conditions
Hydrogen stored as ammonia is much more energy dense per liter than either compressed or liquid hydrogen.
It is also much easier to store as it can be kept at a comparatively low pressure of 10 bar at ambient temperature, vs 700 bar for compressed hydrogen or -253°C for liquid hydrogen


